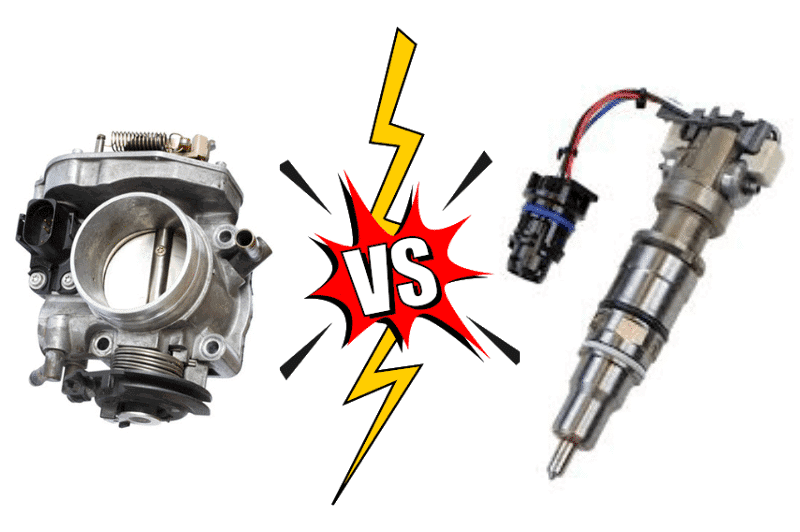
Fuel is supplied to the engine by both the fuel injector and the carburetor. Fuel injector sprays petrol or diesel directly into the engine, whereas carburetor combines air and fuel and feeds the mixture to the engine.
Because of the various mechanisms used in these components, the amount of fuel supply varies as well.
Still, which is better in a motorcycle: a fuel injector or a carburetor? Because of their high power output, engine speed, efficiency, and low emissions, fuel injectors provide superior performance.
Carburetors, on the other hand, require little maintenance, are simple to replace, and are inexpensive.
An injector is the best option for high performance. If you have a limited budget, a carburetor is the best option.
Before delving into the performance characteristics of the fuel injector and carburetor, it’s important to understand how these components work in a motorcycle.
Carburetor or a fuel injector?
The air and fuel are mixed in a carburetor, and the mixture then enters the engine.
The air and fuel mix in a fuel injector only after entering the engine, where the petrol or diesel is sprayed into the engine by the fuel injector.
The carburetor operates through mechanical linkages and components. The desired air-fuel ratio is set manually, and mechanical components control the air-fuel mixture based on the ratio.
An ECU (Electronic Control Unit) controls the injector, which determines the amount of fuel sprayed into the engine and, thus, the air-fuel ratio in the engine.
The ratio is calculated using data obtained by the ECU from various sensors.
These sensors include the throttle position sensor, the crankshaft position sensor, the camshaft position sensor, and so on. These sensors continuously send data to the ECU.
And the ECU dynamically determines the ratio based on engine load, speed, riding conditions, engine temperature, throttle response, and so on.
All of this is automated and controlled electronically. The air-fuel ratio is dynamically controlled by the ECU rather than being manually set.
Now that we understand how these two components work, let us compare their performance against various parameters.
Diesel or petrol efficiency, engine performance, maintenance and repair, cold start, replacement, durability, emissions, and cost are all factors to consider.
Fuel Efficiency
There is no dynamic ratio adjustment because the carburetor mixes a fixed amount of petrol or diesel into the air-fuel mixture based on its tuning.
However, in the fuel injectors, the ECU changes the ratio on a regular basis by varying the amount of fuel entering the engine based on information from its sensors.
As a result, fuel is managed much better in fuel injection systems. As a result, gas efficiency is higher than on carbureted motorcycles.
Repair & Maintenance
Carburetors are powered by a mechanical system. Even the most inexperienced rider can perform carburetor maintenance, repair, and tuning.
However, the fuel injector is a relatively new system.
Complicate matters even more by including the ECU components that control the petrol or diesel spraying into the engine.
The injection system is far more complicated and cannot be easily handled by the average motorcycle rider. Repair and maintenance must be performed by professionals in bike service centers.
As a result of these advantages, carburetors are much easier to repair and maintain than fuel injectors.
Final Thoughts
There are advantages and disadvantages to both carburetors and fuel injection systems.
Where carburetors are cheaper and easier to fix, fuel injection systems are more efficient and offer more consistent combustion.
Although they are more expensive, their high reliability and fuel economy makes them the most common fuel delivery system in use today.